I like to embellish events when it comes to SAP, business, and future, but usually, it comes true in a while. Everything goes simple and complex simultaneously. Business rules go to ease, underlying systems and mechanisms go to complexity. I’m looking at SAP SuccessFactors and wondering how business discards their on-premise strong and robust solutions for SAP SF, which is that simple, like a child and adult. It’s not about reliability, user experiences, but more about processes, that business know-how, and best practices which make you unique on the market. The lyrics are over. The trend to SF dictates new rules for classic SAP consultants and developers. There is almost no ABAP, custom reports, SmartForms, and user-exits. New functional paradigm is to become a technical support and developer guy in a one person, who supports already made up decision by vendor, and develops extentions for business customers. Open-source techniques came to SAP world in terms on clouds, Angular, WebIDE, Splash, Build, jScript, jQuery, REST, LESS, etc. These are the commons we need to learn to be able to serve customers.
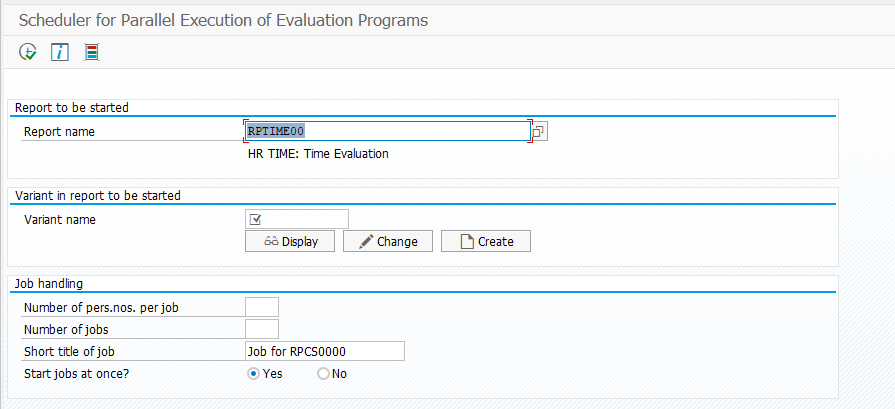
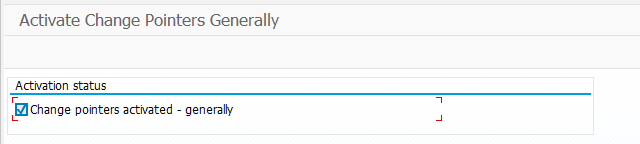
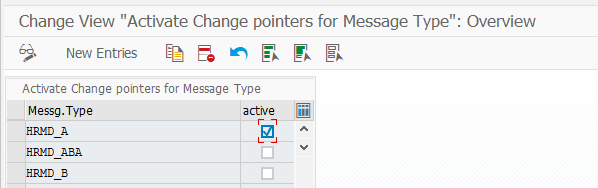
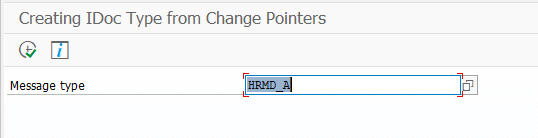
I spent some hours to understand my future and here is what I see. This is a microprototype for my microunderstanding what I was trying to say in the paragraph above.
Read More